Oct 28, 2025 / Author: China Glutathione suppliers & NMN manufacturers
In any living cell, NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) plays an irreplaceable role as a key coenzyme in energy metabolism.
More and more studies have confirmed that increasing the level of NAD+ in organisms has multiple health effects such as prolonging life and improving aging symptoms.
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) is a direct precursor of NAD+, which means that it can be converted into NAD+ in just one step within cells.
Supplementing NMN is a relatively high way to increase the bioavailability of NAD+, and various brands and dosages of NMN supplements have emerged on the market.
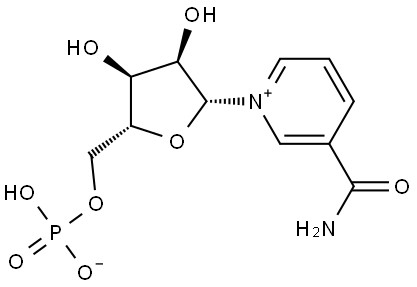
NMN (Nicotinamide mononucleotide). From the perspective of chemical structure, NMN is composed of a phosphate group, a ribose and a nicotinamide base.
As people age, the level of NAD+ in the human body gradually decreases. Therefore, people hope to increase the level of NAD+ by supplementing NMN.
In 2016, Professor Shinichiro Imai's research team from the University of Washington fed NMN (300mg/kg) to mice and found that the NMN level in their plasma rose rapidly within 10 minutes and then dropped quickly.
Meanwhile, the level of NAD+ in plasma has gradually increased, proving that NMN can be rapidly absorbed by the body and converted into NAD+2.
In 2019, the team led by Shinichiro Imai further discovered that the absorption of NMN mainly takes place in the small intestine. A protein called "S1c12a8" in small intestinal cells is responsible for "transporting" NMN into the bloodstream.
One of the key roles of NAD+ in living organisms is to assist in the production of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate).
As the "energy currency" shared by all living beings, ATP has many synthetic pathways, among which the most important one is the "tricarboxylic acid cycle" that oxidizes and decomposes glucose, and NAD+ and its reduced state NADH play a key role in electron transport precisely in this process.
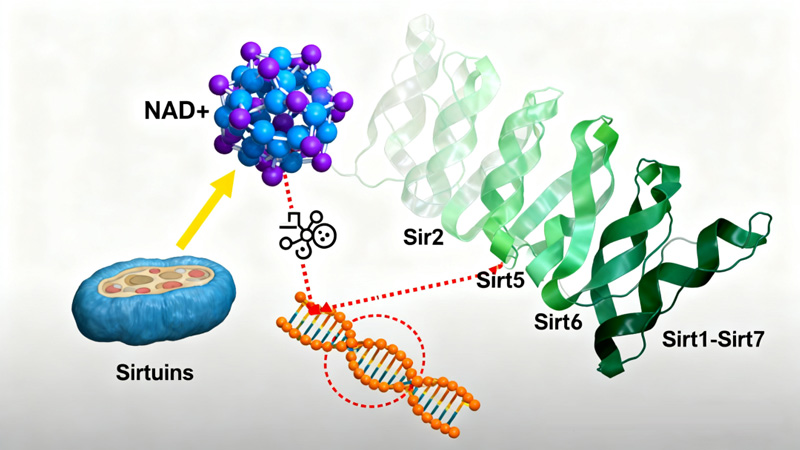
NAD+ is not only a key coenzyme in the process of energy metabolism, but also undergoes various biochemical interactions with over 400 proteins. Among them, a protein family known as Sirtuins plays a crucial regulatory role in multiple aspects such as cell metabolism, inflammation, and damage repair.
The full name of Sirtuins is "Silence Information Regulator", which is composed of seven enzymes including Sirt1-Sirt7.
All of them require NAD+ as a coenzyme to function.
As early as 2011, scientists discovered that activating the Sirt1 protein in mice could reverse insulin resistance caused by a high-fat diet, and this was achieved by orally supplementing NMN to increase NAD+.
In addition to Sirtuins, the key protein PARPs (Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase) that controls DNA repair is also regulated by NAD+.
When external forces such as chemicals and radiation cause DNA breaks in cells, PARPs will bind to the DNA and, with the help of other DNA repair enzymes, start to synthesize new DNA strands.
Many common foods in daily life contain NMN, but the content is relatively low.
Edamame: One of the highest sources of NMN in plants, with approximately 0.47 to 1.88 milligrams per 100 grams. The proportion of β-NMN isomers in fresh edamame exceeds 95%.
Broccoli: Each 100 grams contains 0.25 to 1.12 milligrams, with the stem part having a significantly higher content than the corolla (about 30% higher). Light blanching (blanching for 1 minute) can retain over 80% of its activity, and the effect is even better when eaten raw.
Cucumber: The NMN content in the outer skin is prominent, approximately 0.16 milligrams per 100 grams. After the whole fruit is homogenized, it needs to be purified through an HLB solid-phase extraction column to eliminate the interference of chlorophyll.
Cabbage: Each 100 grams contains 0.0 to 0.90 milligrams, with significant variations among varieties. The content in purple cabbage is usually higher than that in green varieties.
Avocado: Each 100 grams contains 0.36 to 1.60 milligrams. The higher the maturity (when the skin turns black), the NMN content increases by approximately 20%. It needs to be extracted by ultrasonic waves with a 5% methanol water solution (power 400W, time 15 minutes).
Tomatoes: Each 100 grams contain 0.26 to 0.30 milligrams. Heating (such as cooking) can cause about 40% degradation of NMN. It is recommended to eat them raw or cook them slowly at a low temperature.
Raw beef: Each 100 grams contains 0.06 to 0.42 milligrams. The content in red meat is higher than that in white meat. Freezing storage (-20℃) can reduce degradation.
Shrimp: Each 100 grams contains 0.22 milligrams. The NMN content in shrimp meat is three times that of shrimp shells. A mixed anion exchange column is needed to remove chitin impurities.
Mushrooms: Each 100 grams contain 0.0 to 1.01 milligrams, with the highest content in Pleurotus ostreatus. After drying, the concentration can be increased to three times that of fresh products.
Whole grains: Oats and barley contain 0.1 to 0.5 milligrams per 100 grams. They need to be extracted with a 0.1% formic acid methanol solution and separated through a C18 chromatographic column.
The NMN directly consumed in daily diet is not sufficient to affect its level in the human body.
The NMN in the human body is mainly synthesized from two substances: one is NAM (nicotinamide), and the other is NR (nicotinamide riboside).
After NMN is synthesized, it only needs to undergo one more reaction to be transformed into NAD+ and exert its biological efficacy.
The "used" NAD+ will not be "thrown away" by the human body, but will be degraded into NAM and recycled.
This triangular cycle composed of NAM, NMN and NAD+ is also known as the "salvage" pathway for NAD+ synthesis and is the most important way to maintain NAD+ levels in the human body.
NMN is a substance that naturally exists in the human body and is the direct precursor of NAD+. Supplementing NMN can increase the level of NAD+ in the body, help cells produce energy (ATP), and also activate a series of proteins that consume NAD+, achieving effects such as DNA repair and maintaining cell health.
Supplier Introduction: China glutathione supplier and NMN manufacturer GSHworld, the company mainly develops biotechnology and industrialization. As a global pioneer in enzymatic catalytic ATP regeneration technology, our company advocates green production and is committed to providing customers with better and more environmentally friendly products and services. Glutathione Manufacturer,NMN Factory,Citicoline Sodium supplier,China NMN manufacturers
No previous
+86-755-23577295
+86 18718790084
Room 832, Building 12, Shenzhen Bay Science and Technology Ecological Park, Yuehai Street, Nanshan District, Shenzhen China